This guide provides comprehensive instructions on how to compile gSender from its source code for various operating systems, including Windows, macOS (Intel & Apple Silicon), and Linux (including Raspberry Pi). Building from source allows you to contribute to development, test experimental features, or customize the application for your specific needs.
Note: This guide is intended for users with some familiarity with command-line interfaces and software development environments. If you are looking to simply install gSender, please refer to the gSender Installation Guide.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have the following software installed on your system. Version numbers are critical for Node.js and Yarn.
1. Git
Git is essential for cloning the gSender repository.
- Windows: https://git-scm.com/downloads
- macOS:
- Install via Homebrew:
brew install git - Or download directly from https://git-scm.com/downloads
- Install via Homebrew:
- Linux:
sudo apt-get install git
2. Node.js, npm (Node Package Manager) and Yarn
gSender is a JavaScript/TypeScript application. Node.js and its package manager (npm) are crucial.
-
Recommended Version: gSender is built using Node.js version 20.x.
-
Windows Installation:
- Download and install Chocolatey:
powershell -c "irm https://community.chocolatey.org/install.ps1|iex" - Download and install Node.js:
choco install nodejs --version="20.19.5" - Verify the Node.js version:
node -vShould print “v20.19.5”.
- Download and install Yarn:
corepack enable yarn - Verify Yarn version:
yarn -v
- Download and install Chocolatey:
-
macOS Installation:
- Download and install nvm:
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.40.3/install.sh | bash - Source the shell (in lieu of restarting):
. "$HOME/.nvm/nvm.sh" - Download and install Node.js:
nvm install 20 - Verify the Node.js version:
node -vShould print “v20.19.5”.
- Download and install Yarn:
corepack enable yarn - Verify Yarn version:
yarn -v
- Download and install nvm:
-
Linux Installation:
- Download and install nvm:
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.40.3/install.sh | bash - Source the shell:
. "$HOME/.nvm/nvm.sh" - Download and install Node.js:
nvm install 20 - Verify the Node.js version:
node -vShould print “v20.x.x”.
- Download and install Yarn:
corepack enable yarn - Verify Yarn version:
yarn -v
- Download and install nvm:
3. Python
Python is often required for Electron’s native module compilation (via node-gyp).
-
Recommended Version: Python 3.x is generally expected.
-
Windows Installation:
- Download Python
- Ensure Python is added to your system’s PATH during installation.
-
macOS Installation:
- Python 3 is typically pre-installed or easily installed via Homebrew.
- Install
setuptools:sudo -H pip install setuptools
-
Linux Installation:
- Download Python (or use your system’s package manager like
sudo apt-get install python3)
- Download Python (or use your system’s package manager like
4. C++ Compiler & Build Tools
These tools are necessary for compiling native Node.js modules that gSender and its dependencies rely on. The CI workflow explicitly adds node-gyp globally.
- Windows:
- Run
npm install --global --production windows-build-toolsto set up necessary tools.
- Run
- macOS:
- Install Xcode Command Line Tools:
xcode-select --install - Ensure
setuptoolsfor Python is installed:sudo -H pip install setuptools - For Apple Silicon (M1/M2/M3 chips):
- While Node.js and Electron increasingly support ARM64 natively, some older native modules might still require Rosetta 2. If you face persistent
node-gyperrors, try running your terminal via Rosetta (Right-click Terminal.app -> Get Info -> “Open using Rosetta”). However, aim for nativearm64builds if possible. - A crucial step often overlooked is ensuring that
node-gyphas the correct path to the Python executable, especially if you have multiple Python versions. Settingexport PYTHON=/usr/bin/python3or similar can help.
- Install Xcode Command Line Tools:
- Linux (and Raspberry Pi):
- Install
build-essential:sudo apt update sudo apt install build-essential git libusb-1.0-0-dev pkg-config libudev-dev libgtk-3-dev libudev-devandlibgtk-3-devare crucial for compiling certain native modules on Linux.- Raspberry Pi / Debian-based systems: You will likely need additional runtime libraries for Electron to run correctly, especially on headless or minimal installations.
libappindicator3-1: This is a common missing dependency used by gSender.sudo apt install libappindicator3-1- Other common Electron dependencies:
sudo apt install libgconf-2-4 libnss3 libasound2 libsecret-1-0 libgtk-3-0 - Architecture considerations (Raspberry Pi): gSender is typically built for
arm64(AArch64). If you are on an older Raspberry Pi OS (likearmhfon 32-bit systems) or a different ARM architecture, you might encounter issues. Modern Raspberry Pi OS (64-bit) is strongly recommended for native compilation. Cross-compilation is generally not well-supported and can be problematic as reported in community forums.
- Install
Cloning the Repository
First, you need to get the gSender source code.
- Open your terminal or command prompt.
- Navigate to the directory where you want to store the gSender project.
- Clone the repository and enter the directory:
git clone https://github.com/Sienci-Labs/gsender.git cd gsender
Installing Dependencies
Once the repository is cloned, install the project’s dependencies using Yarn.
- Clean previous builds (optional but recommended):
Thepackage.jsonscriptpreparerunsnpm run clean.yarn prepareThis command typically cleans out old build artifacts (
./distand./outputdirectories) and prepares the environment. - Install main dependencies:
yarn installThis command downloads and installs all required Node.js packages as defined in
package.jsonandyarn.lock. This step can take some time and may compile native modules.
Development Workflow
These commands are ideal for active development, offering features like hot-reloading for faster iteration.
- Run in Development Mode (Hot Reloading):
yarn devThis launches the local development server. Please open gSender in your browser at http://localhost:8000.
Any changes you make to the source code will automatically reload. - Clean previous builds (optional but recommended):
yarn cleanRemoves old build artifacts and prepares a clean environment for a fresh build.
Production / Release Build Workflow
These commands are used to create optimized, distributable versions of gSender for your operating system.
- Build the Production Application:
yarn buildThis compiles the app for production into the
distdirectory.
It includes minification and optimization suitable for release. - Build OS-specific Packages:
yarn build:windowsyarn build:macosyarn build:linux
Each command produces a platform-specific package (e.g.,.exe,.dmg,.AppImage, or.deb).
- Build Electron Package (Cross-platform builder):
yarn electron-builderUses Electron Builder to create a standalone installer.
The output (e.g.,.exe,.dmg,.AppImage,.zip) will appear in theoutput/folder.
Raspberry Pi (ARM) Specific Build
The gSender’s CI has a dedicated job for building Raspberry Pi packages, which uses a Docker-based approach for consistency and environment control. For Pi 5 and other 64-bit Raspberry Pi models, native ARM64 compilation is the recommended approach over cross-compilation.
- Inspect the Pi Build Script: The CI executes
scripts/build-pi.sh. It’s recommended to examine this script and the associatedDockerfilePiin the project root for the most accurate and up-to-date instructions for building on a Raspberry Pi. - Using Docker (Recommended for Pi):
If you have Docker installed on your Raspberry Pi or a cross-compilation environment, you can use the provided Docker setup (ensuring you are in the gSender root directory):./scripts/build-pi.shThis script will build a Docker image and then use it to compile gSender for the Raspberry Pi’s ARM architecture. This approach helps encapsulate all dependencies and ensures a reproducible build environment.
- Native Compilation on Raspberry Pi (64-bit OS):
If you choose to compile directly on a Raspberry Pi running a 64-bit OS (e.g., Raspberry Pi OS (64-bit)), follow the general Linux instructions, ensuring all prerequisites (especially Node.js 20.xarm64and theapt installdependencies) are met. Some users have successfully compiled on Pi 5 by following these steps.- Verify your Node.js architecture:
node -p "process.arch"should outputarm64. - Ensure all necessary dev libraries are installed:
sudo apt update && sudo apt install build-essential git libusb-1.0-0-dev pkg-config libudev-dev libgtk-3-dev libappindicator3-1 libgconf-2-4 libnss3 libasound2 libsecret-1-0 libgtk-3-0
- Verify your Node.js architecture:
Common Troubleshooting
Here are some common issues you might encounter when compiling gSender locally, along with potential solutions, drawing from community experiences and CI practices. If you can’t find your particular issue, you can always reach out in our Community Forum or GitHub or try these general debugging steps:
- Read Error Messages Carefully: The error messages often contain clues about the root cause.
- Search for Specific Errors: Copy and paste unique error messages into a search engine (or the Sienci Labs Forum) to find known solutions.
- Check GitHub Issues: Review the gSender GitHub repository’s issues page for similar problems, especially those tagged “build issue.”
- Start Fresh: If you’re stuck, delete the entire
gsenderdirectory, re-clone, and follow the steps from the beginning. - Docker: If you continue to have environment issues, consider using Docker for a consistent build environment, similar to how Sienci Labs builds their releases, especially for Linux/ARM targets.
bash Command Not Found on Windows
-
Problem: When running
yarncommands (e.g.,yarn run dev,yarn clean,yarn prepare), you may see an error like'bash' is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file.
This occurs because severalpackage.jsonscripts invokebash -c "...", which isn’t supported natively in Windows Command Prompt or PowerShell. -
Solution:
- Run from Git Bash (Recommended):
The easiest and most reliable solution is to use the Git Bash terminal that comes with Git for Windows.
Open Git Bash (search for it in your Start Menu) and execute allyarnand othergSendercommands referenced in this documentation, from within that terminal. This ensures full compatibility with commands used in the build scripts - Add Git to System PATH (Advanced):
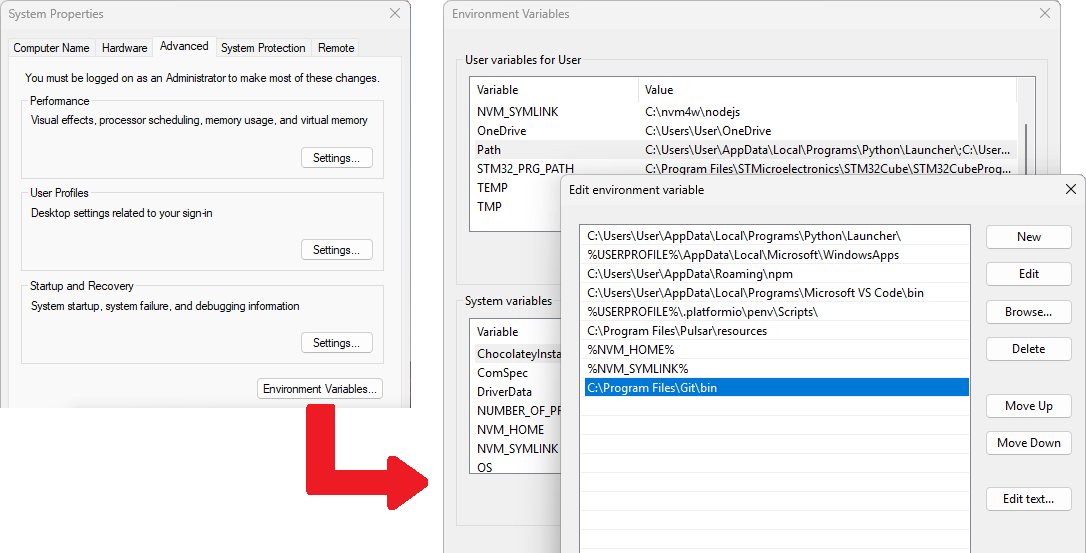
If you prefer using PowerShell or Command Prompt, you can makebashavailable system-wide:- Search for “Environment Variables” in the Start Menu and select Edit the system environment variables.
- Click Environment Variables… → under System variables, find and edit
Path. - Add a new entry:
C:Program FilesGitbin
(or your actual Git install path). - Save your changes and restart your terminal.
After this,bashshould work in PowerShell or CMD.
- Use Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL):
For a full Linux-like environment, you can install WSL and a distribution such as Ubuntu, then clone and build gSender entirely from there.
- Run from Git Bash (Recommended):
Node.js / Yarn Version Mismatches or Corrupted Installs
- Problem: Errors during
yarn installrelated to package resolution,node-gyp, or general build failures. - Solution:
- Check Node.js Version: Ensure you are using Node.js 20.x as specified. Use
node -vandnvm ls(if using nvm). If incorrect, switch usingnvm use 20. Some community guides for Raspberry Pi may suggest Node.js 18.x, but the official CI uses 20.x. - Check Yarn Version: Ensure you are using
yarn@1.22.22. Install globally withnpm install --global yarn@1.22.22. - Clear Caches:
yarn cache clean npm cache clean --force - Clean and Reinstall:
rm -rf node_modules yarn.lock package-lock.json yarn install
- Check Node.js Version: Ensure you are using Node.js 20.x as specified. Use
Native Module Compilation Errors (node-gyp)
This is a very common source of issues, often manifesting as errors during yarn install or yarn build that mention node-gyp, Python, or C++ compilers.
- Problem:
gyp ERR! build error,Could not find any Visual Studio installation,Command 'python' not found, etc. - Solution:
- Ensure C++ Build Tools are Installed: Refer to “C++ Compiler & Build Tools” in the Prerequisites section for your operating system.
- Windows: Verify Visual Studio Build Tools and potentially
vcredist2017are installed. - macOS: Ensure Xcode Command Line Tools are installed (
xcode-select --install) andpip install setuptoolshas been run. If you have multiple Python versions, explicitly set thePYTHONenvironment variable to point to Python 3 (e.g.,export PYTHON=/usr/bin/python3) before runningyarn installorelectron-rebuild. - Linux: Make sure
build-essential,libudev-dev, andlibgtk-3-devare installed (sudo apt install build-essential libudev-dev libgtk-3-dev). - Python Path: Ensure Python 3.x is installed and correctly added to your system’s PATH. On some systems, you might need to explicitly link
pythontopython3. - Rebuild Electron Native Modules: Sometimes, modules need to be explicitly rebuilt against your specific Electron version.
yarn run electron-rebuild - macOS Apple Silicon (M1/M2/M3) Specific: If you still face issues with native modules after confirming Node.js
arm64andxcode-select, consider deletingnode_modulesandyarn.lock, then reinstalling. Ifnode-gypstruggles, ensure Python 3 is properly set up and linked. Sometimes, trying to build within a terminal running under Rosetta 2 (if you’re having trouble with anarm64native module) can be a temporary workaround, though native ARM64 is preferred.
yarn prepare / Native Dependency Issues
- Problem: The
yarn preparecommand (which runsnpm run cleanand potentiallyprebuild-latest) fails, or after running it, you still get runtime errors like “Cannot find module…” for native dependencies (e.g.,@serialport/bindings). This is a common build issue. - Solution:
- Ensure
yarn preparecompleted successfully: This step is crucial for copying prebuilt or compiled native modules to the correct location for Electron. If it failed, review the output for specific errors related to permissions, missing files, or compilation failures. - Manual Copying (Workaround): In rare cases, the script might not correctly copy the compiled native modules to the expected Electron
distdirectory. Verify that thegsender/src/node/modulesdirectory (which holds prebuilt binaries for certain dependencies) exists and its contents are correctly placed in your build output.
- Ensure
Missing libappindicator3-1 and other Electron Runtime Dependencies (Linux / Raspberry Pi)
- Problem: On minimal Linux installations (like some Raspberry Pi OS variants or older Pi OS versions like Raspberry Pi 4 (2GB)), gSender might fail to launch with errors related to
libappindicator3-1or other GTK/UI libraries. This is a frequently reported issue on Raspberry Pi. - Solution: Install the missing libraries as outlined in the “Prerequisites – Linux” section:
sudo apt update sudo apt install libappindicator3-1 libgconf-2-4 libnss3 libasound2 libsecret-1-0 libgtk-3-0
Architecture Mismatches and Raspberry Pi Specifics
- Problem: Issues running gSender on Raspberry Pi or other ARM devices, especially older ones, due to incorrect architecture (e.g., 32-bit
armhfvs. 64-bitarm64). Cross-compilation is often problematic. - Solution:
- Use 64-bit OS: For Raspberry Pi 3/4/5 and other compatible ARM devices, use a 64-bit operating system (e.g., Raspberry Pi OS (64-bit)). gSender is typically built for
arm64. - Native Compilation: Focus on compiling directly on the ARM64 device rather than attempting cross-compilation, which often leads to errors.
- Consult
scripts/build-pi.shandDockerfilePi: For specific ARM build challenges, the project’s dedicated Raspberry Pi build script and Dockerfile are the authoritative sources.
- Use 64-bit OS: For Raspberry Pi 3/4/5 and other compatible ARM devices, use a 64-bit operating system (e.g., Raspberry Pi OS (64-bit)). gSender is typically built for
@electron/remote Not Found at Runtime
- Problem: After building, the application fails to launch or encounters errors related to
@electron/remote. Thepackage.jsonincludes@electron/remoteinextraResourcesforelectron-builder, indicating it’s handled during the packaging process. - Solution: While less common with proper
yarn installandyarn prepareexecution, sometimes@electron/remotemight still be an issue. If so, afteryarn build(oryarn build-latest), navigate into the build output directory (e.g.,dist/gsenderorbuild) and install it manually:# Assuming your build output is in 'dist/gsender' (as per "build.directories.app" in package.json) cd dist/gsender npm install --save @electron/remote cd ../.. # Return to root project directory
Disk Space or Long Path Issues (Windows)
- Problem: On Windows, deep directory structures can exceed the maximum path length, causing issues during dependency installation.
- Solution: Enable long path support in Windows (requires registry modification or Group Policy). Also, ensure you have sufficient disk space.
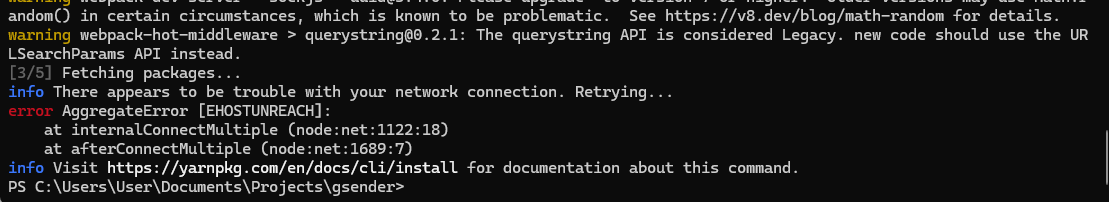
Network Issues (Firewall/Proxy)
- Problem:
yarn installfails to download packages. - Solution: Check your firewall or proxy settings. Ensure
npmandyarnare configured to use your proxy if applicable.npmandyarnneeds access to the internet to download and install dependencies.
Contributing
If you’ve successfully built gSender and found a solution to an unlisted problem, consider contributing to the project or creating a Pull Request to improve this documentation. Your contributions help the entire community!
